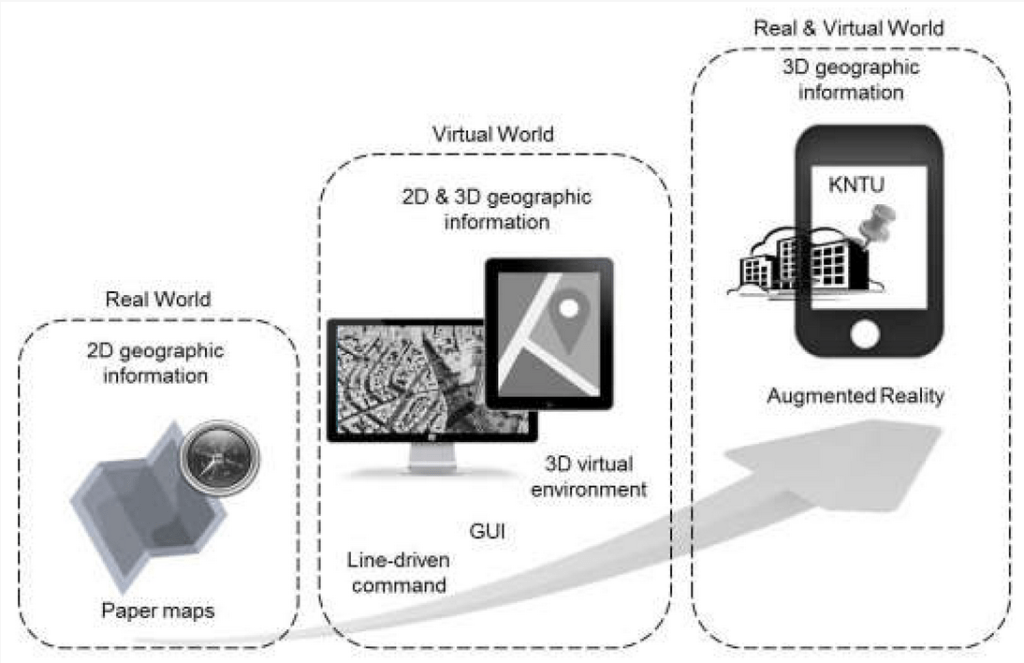
What is 3D Tracking?

In the rapidly evolving world of technology, 3D tracking has emerged as a groundbreaking solution that bridges the gap between the digital and physical realms. It has revolutionized various industries, from entertainment and gaming to robotics and augmented reality. By enabling devices to perceive and understand the three-dimensional space around them, 3D tracking empowers them to interact with the real world in unprecedented ways. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of 3D tracking, exploring its fundamental concepts, applications, and the transformative impact it has on our daily lives.
DIGITAL COMPOSITING: 3d Camera Tracking with Matchmover.
Understanding 3D Tracking:
At its core, 3D tracking involves capturing and analyzing the motion and position of objects or subjects within a three-dimensional space. It leverages a combination of hardware and software techniques to estimate and track the movement of objects in real-time. By accurately mapping the physical world onto digital representations, 3D tracking enables devices to perceive depth, distance, and spatial relationships, providing a more immersive and interactive experience.
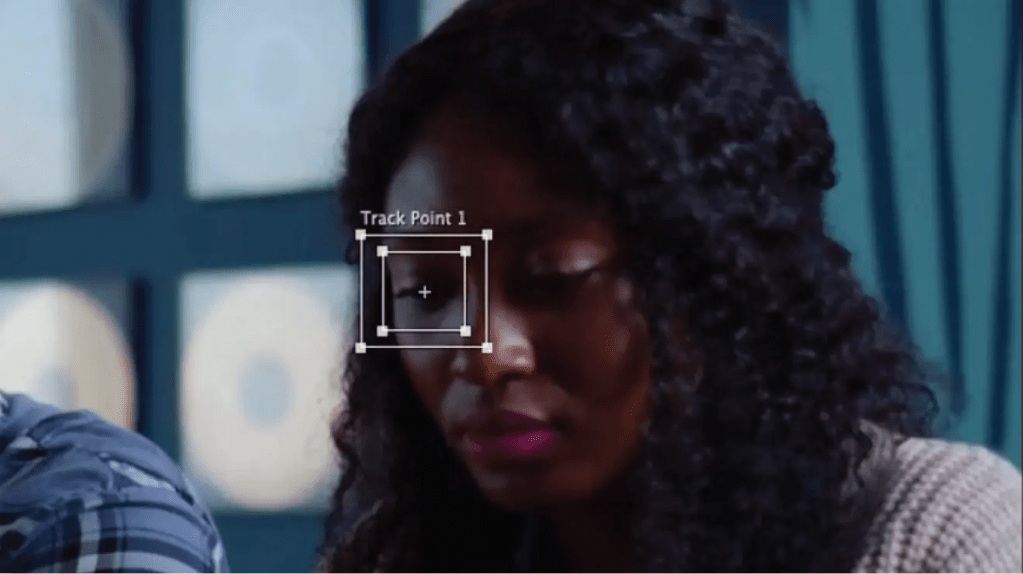

Techniques and Technologies:
Several techniques and technologies contribute to the advancement of 3D tracking. Let’s explore a few prominent ones:
- Sensor-based Tracking: This approach utilizes various sensors such as cameras, depth sensors, accelerometers, and gyroscopes to capture data and estimate the position and orientation of objects. Computer vision algorithms analyze the collected data to reconstruct the 3D scene and track the objects within it.
- Marker-based Tracking: In this technique, predefined markers with known patterns are placed on objects or subjects of interest. The cameras or sensors detect these markers, allowing for precise tracking of their position and movement. Marker-based tracking is widely used in applications like motion capture and industrial robotics.
- Markerless Tracking: Unlike marker-based tracking, markerless tracking relies on computer vision algorithms to detect and track objects without the need for physical markers. It uses features like object recognition, optical flow, and pattern matching to identify and track objects in a scene. Markerless tracking finds applications in augmented reality, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.

3D Motion Tracking Application Technique
Applications of 3D Tracking:
The applications of 3D tracking span across numerous industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities. Here are some notable examples:
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR applications heavily rely on 3D tracking to overlay virtual objects onto the real world. By precisely tracking the user’s surroundings, AR devices can seamlessly blend digital content with the physical environment, creating immersive experiences for gaming, education, architecture, and more.
- Robotics and Automation: 3D tracking enables robots to perceive their environment accurately, enhancing their ability to manipulate objects, navigate autonomously, and interact with humans in a safer and more intuitive manner. Industrial robots, drones, and autonomous vehicles leverage 3D tracking to perform complex tasks efficiently.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, 3D tracking plays a vital role in surgical planning, navigation, and medical imaging. Surgeons can visualize patient anatomy in real-time and accurately track surgical instruments, leading to improved precision, reduced invasiveness, and enhanced patient outcomes.
- Sports and Entertainment: 3D tracking has revolutionized the sports and entertainment industry by providing real-time analysis, immersive experiences, and enhanced audience engagement. Tracking technologies enable precise motion capture for animation and visual effects, as well as advanced sports analytics for performance evaluation and training.
An Introduction to 3D Object Tracking (Advanced) check This out!
As technology continues to advance, 3D tracking has become a transformative force, unlocking new possibilities across various domains. By endowing devices with spatial awareness, it enables them to interact with the physical world in a more intuitive and intelligent manner. The applications of 3D tracking are vast and ever-expanding, ranging from augmented reality and robotics to healthcare


Leave a comment