- The Gut: More Than Just a Digestive Organ
- Enter the Microbiome
- The Gut-Brain Axis: A Bidirectional Communication Highway
- The Impact on Mental Health
- The Influence on Physical Health
- Harnessing the Power of the Gut-Brain Connection
When it comes to understanding the complexities of the human body, the gut and the brain have long been regarded as distinct entities. However, emerging scientific research has unveiled a remarkable connection between these two organs, revealing a dynamic relationship that influences our overall well-being. This connection, known as the gut-brain connection, highlights the intricate interplay between the gut and the brain, revolutionizing our understanding of various aspects of human health. In this blog post, we will dive into the fascinating world of the gut-brain connection, exploring its significance and the implications it has for our mental and physical well-being.
The Gut: More Than Just a Digestive Organ
Traditionally seen as a system responsible for digestion and nutrient absorption, the gut, or gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is an extensive network of organs, including the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. It plays a crucial role in breaking down food, extracting nutrients, and eliminating waste from our bodies. However, recent research has shown that the gut is much more than a mere digestive organ.
Enter the Microbiome
At the heart of the gut-brain connection lies the gut microbiome, a vast and diverse community of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. These tiny inhabitants play a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance within our gut and exert a profound influence on our overall health.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Bidirectional Communication Highway
The gut and the brain are connected through a complex network of biochemical signaling pathways, collectively referred to as the gut-brain axis. This axis allows bidirectional communication between the two organs, enabling them to exchange information and influence each other’s functions.
One important component of this communication is the vagus nerve, a major nerve that connects the brain with various organs, including the gut. Through this pathway, signals and chemical messengers travel back and forth, influencing a range of physiological processes, such as digestion, mood regulation, immune function, and even cognitive abilities.
The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems
The Impact on Mental Health
The gut-brain connection has been linked to mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Research suggests that alterations in the gut microbiome can lead to changes in the production of neurotransmitters (chemical messengers in the brain), affecting mood and behavior. Additionally, the gut microbiota can produce metabolites that directly influence brain function, further emphasizing the connection between the gut and mental well-being.
The surprising link between your microbiome and mental health
The Influence on Physical Health
Beyond mental health, the gut-brain connection also plays a vital role in various physical health conditions. Studies have shown that imbalances in the gut microbiome are associated with gastrointestinal disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even obesity. Furthermore, emerging evidence indicates that the gut microbiota may impact immune responses, inflammation, and metabolism, contributing to the development of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders.
The influence of physical activity on mental well-being
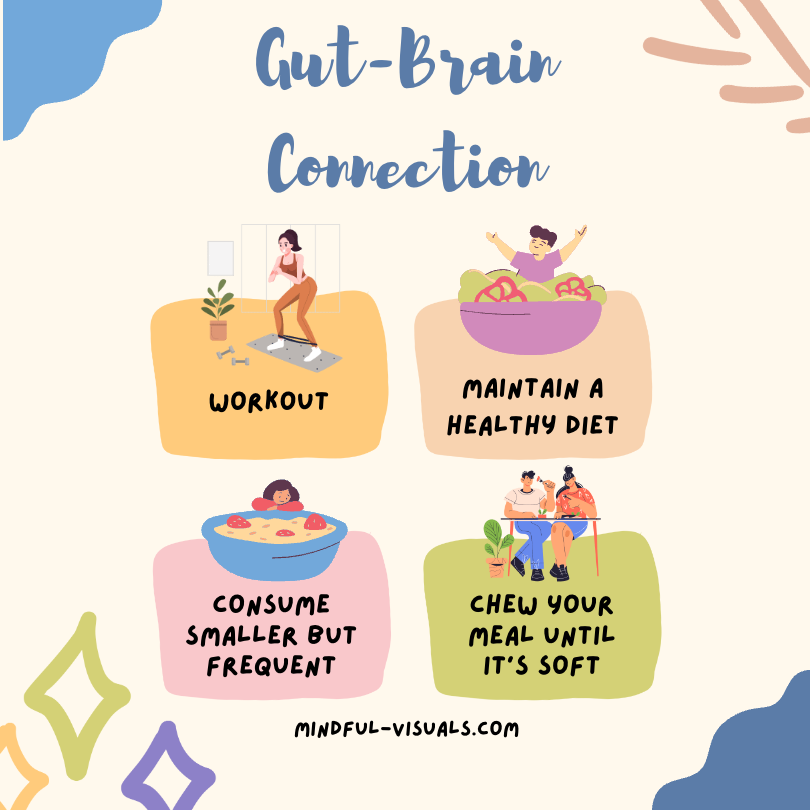
Harnessing the Power of the Gut-Brain Connection
Understanding the gut-brain connection opens up exciting avenues for potential interventions and therapies. Probiotics, prebiotics, and dietary modifications are being explored as means to positively influence the gut microbiome and subsequently improve mental and physical health outcomes. Additionally, mind-body practices such as meditation and stress reduction techniques have shown promise in positively modulating the gut-brain axis.
Gut feelings: harnessing the gut-brain connection to improve mood
The gut-brain connection represents a remarkable frontier in scientific research, revolutionizing our understanding of the human body and challenging the conventional separation between mental and physical health. The bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain holds immense potential for novel therapeutic approaches and interventions in the field of psychiatry, gastroenterology, and overall well-being. As research continues…

Leave a reply to Surprising Connection Between Diet and Mood – Mindful-Visuals Cancel reply